What are currency pairs?
In the foreign exchange market, currency is traded in pairs. Pairs have meaning in relation to each other so must always stay together.
The two currencies in a pair are traded one against the other. The rate at which they are traded is called the exchange rate. The exchange rate is affected by currency supply and demand.
Most common currencies
The most common currencies traded in the market are called ‘majors’. Most currencies are traded against the United States dollar (USD). USD is traded more than any other currency. The five currencies most traded next are: the euro (EUR); the Japanese yen (JPY); the British pound sterling (GBP); the Swiss franc (CHF), and the Australian dollar (AUD). Trades of the six major currencies total 90% of the market.
The most common currency pair is EUR/USD.
The exchange rate
The exchange rate is always changing. The value of one currency is determined by market supply and demand forces, by comparing it to another currency. In a currency pair, the first currency is called the ‘base currency’; the second currency is called the ‘quote currency’ or ‘counter currency’.
When you buy a currency pair, you buy the base currency and sell the quote currency. The exchange rate tells buyers how much of the quote currency they need to buy one of the base currency. The order in a pair always stays the same, being a common approach by the industry. USD/JPY, for example, is a pair (USD = base, JPY = the quote). The order within the pair, in the way you use the term, does not change. So you either BUY it or SELL it, depending on the direction of the trade. For example: USD/JPY – you either BUY JPY using USD or you Sell JPY to get USD. On the currency rate table on the Easy-Forex® website you can view the way in which each pair available for trade is ordered.
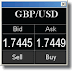
Here is an example: EUR/USD 1.2500 means you need 1.25USD to buy one euro. It also means if you sell one euro you get 1.25USD. All trades involve buying one currency and selling another currency at the same time. If in the next day the Euro is rising against the USD and the exchange rate is now 1.26, for every 1 Euro that you bought, you have earned 1USD cent. Or, if you traded the opposite direction, for every EUR that you sold (at 1.25) you lost 1USD cent (since you “buy” back the EUR for 1.26).
Buy and sell currency
Traders in the foreign exchange market buy and sell currency to try to make profit. There are two prices for currency: the buy price, called the ‘BID’; and the sell price, called the ‘ASK’.
The difference between the ‘bid’ and the ‘ask’ is called the ‘spread’. The spread represents the difference between what the market maker gives to buy from a trader, and what the market maker takes to sell to a trader.
For example: the EUR/USD bid/ask rate is 1.2100/1.2200. The market maker gives $1.21 when buying from the trader, but takes $1.22 when selling to the trader. If traders buy and sell immediately without any change in the exchange rate, they lose money. This happens because of the spread – traders pay more to buy the currency than they receive when they sell in that one moment.
In fact, the spread is the leading source of income for the market maker. Like any other market, the merchant will buy at one price and sell at a higher price.
Quotes
The price of a currency is called the ‘quote’. There are two forms of quotes in the Forex market: direct quotes, and indirect quotes.
A direct quote is the price for one US dollar in terms of another currency.
An indirect quote is the price for one UNIT of another currency in terms of the US dollar.
Please note: in general, most currencies are quoted against the USD (e.g. – “direct quote”).
But, the EUR, GBP, AUD, NZD (as well as Gold XAU and silver XAG) are indirect quoted, for example: GBP/USD.
The quote is the price to a currency pair that the deal will be made with. This is unlike an ‘indication’, where the price given by a market maker is only informational (for trader’s knowledge, rather than for execution). Real time quotes are provided to Easy-Forex® logged in users. Delayed quotes ('indication') are provided to the rest of the site users.
To start getting real time currency quotes, join the Easy-Forex® trading platform for free.
Source: Easy-Forex®
Friday, September 18, 2009
Thursday, September 3, 2009
easy forex, foreign exchange, forex, rewards, risks
Risks and Rewards in the Forex Market
In the Forex market, risks might be great, but the rewards can be great too.
The Forex market is different from other markets. The speed and huge size of the market mean it changes continually. Forex is not the same as any other market in the financial world; it is not able to be controlled. This makes it risky - increased risk means chances for a higher profit, also for higher loss.
There are many different ways to invest in the Forex market. However, before you decide to get involved, you should think about what result you want from your investment and your level of experience. Trading foreign currencies is demanding.
Do not invest money you cannot accept to lose.
What is risk capital?
Risk capital is the money that Easy-Forex® suggests you use for trading in the market. It is money you have that you do not need for day to day living and you can afford to lose.
Can I reduce risk?
You can reduce risk in many different ways. Easy-Forex® has tools to help you make the most of your trading.
First it is important to understand the market. Easy-Forex® has training programs on its website that help you learn about trading. Customers are trained for free. Easy-Forex® believes that good training is necessary for trading success. You can deposit a small amount and do some small trades at first to help you understand how the market operates.
Another way to reduce risk is to try to judge what direction a currency might take by studying what has happened in the market until now and the causes of changes in the market. This is called forecasting. Forecasting helps you to develop an idea what might happen in the market in the near future.
You can also place Stop Loss and Take Profit limits on your trades. This reduces the risk of losing more than you feel comfortable with. Stop Loss and Take Profit help you to control your trading. When you place these limits on your trades, you do not have to watch the computer screen every minute.
Leveraged trading
The leveraged nature of the Forex market means that risks and rewards are higher. Any movement in the market will have an effect on what you win or lose. With leveraged trading, the effect can be increased on a big scale.
You can win a great amount, or you can lose a great amount. This is why it is important to understand the market. It is important to use methods that limit your risk. Learn to be a disciplined trader.
Is foreign exchange trading right for me?
Foreign exchange trading is not the right investment for everyone. If you are responsible and trade to the limits you set for yourself, you will find there are rewards. But you must take risks to get rewards. The risks must be right for you.
Source: Easy Forex
The Forex market is different from other markets. The speed and huge size of the market mean it changes continually. Forex is not the same as any other market in the financial world; it is not able to be controlled. This makes it risky - increased risk means chances for a higher profit, also for higher loss.
There are many different ways to invest in the Forex market. However, before you decide to get involved, you should think about what result you want from your investment and your level of experience. Trading foreign currencies is demanding.
Do not invest money you cannot accept to lose.
What is risk capital?
Risk capital is the money that Easy-Forex® suggests you use for trading in the market. It is money you have that you do not need for day to day living and you can afford to lose.
Can I reduce risk?
You can reduce risk in many different ways. Easy-Forex® has tools to help you make the most of your trading.
First it is important to understand the market. Easy-Forex® has training programs on its website that help you learn about trading. Customers are trained for free. Easy-Forex® believes that good training is necessary for trading success. You can deposit a small amount and do some small trades at first to help you understand how the market operates.
Another way to reduce risk is to try to judge what direction a currency might take by studying what has happened in the market until now and the causes of changes in the market. This is called forecasting. Forecasting helps you to develop an idea what might happen in the market in the near future.
You can also place Stop Loss and Take Profit limits on your trades. This reduces the risk of losing more than you feel comfortable with. Stop Loss and Take Profit help you to control your trading. When you place these limits on your trades, you do not have to watch the computer screen every minute.
Leveraged trading
The leveraged nature of the Forex market means that risks and rewards are higher. Any movement in the market will have an effect on what you win or lose. With leveraged trading, the effect can be increased on a big scale.
You can win a great amount, or you can lose a great amount. This is why it is important to understand the market. It is important to use methods that limit your risk. Learn to be a disciplined trader.
Is foreign exchange trading right for me?
Foreign exchange trading is not the right investment for everyone. If you are responsible and trade to the limits you set for yourself, you will find there are rewards. But you must take risks to get rewards. The risks must be right for you.
Source: Easy Forex
foreign exchange, forex, volatile
Volatality in Forex
Volatility (in Forex trading) refers to the amount of uncertainty or risk involved with the size of changes in a currency exchange rate. A higher volatility means that an exchange rate can potentially be spread out over a larger range of values. High volatility means that the price of the currency can change dramatically over a short time period in either direction.
On the other hand, a lower volatility would mean that an exchange rate does not fluctuate dramatically, but changes in value at a steady pace over a period of time.
Commonly, the higher the volatility, the riskier the trading of the currency pair is.
Technically, the term “Volatility” most frequently refers to the standard deviation of the change in value of a financial instrument over a specific time period. It is often used to quantify (describe in numbers) the risk of the currency pair over that time period.
Volatility is typically expressed in yearly terms, and it may either be an absolute number ($0.3000) or a fraction of the initial value (8.2%).
In general, volatility refers to the degree of unpredictable change over time of a certain currency pair exchange rate. It reflects the degree of risk faced by someone with exposure to that currency pair.
Volatility for market players
Volatility is often viewed as a negative in that it represents uncertainty and risk. However, higher volatility usually makes Forex trading more attractive to the market players. The possibility for profiting in volatile markets is a major consideration for day traders, and is in contrast to the long term investors’ view of buy and hold.
Volatility does not imply direction. It just describes the level of fluctuations (moves) of an exchange rate. A currency pair that is more volatile is likely to increase or decrease in value more than one that is less volatile.
For example, a common “conservative” investment, like in savings account, has low volatility. It will not lose 30% in a year but neither will it profit 30%.
Volatility over time
Volatility of a currency pair changes over time. There are some periods when prices go up and down quickly (high volatility), while during other times they might not seem to move at all (low volatility).
Source: Easy Forex
On the other hand, a lower volatility would mean that an exchange rate does not fluctuate dramatically, but changes in value at a steady pace over a period of time.
Commonly, the higher the volatility, the riskier the trading of the currency pair is.
Technically, the term “Volatility” most frequently refers to the standard deviation of the change in value of a financial instrument over a specific time period. It is often used to quantify (describe in numbers) the risk of the currency pair over that time period.
Volatility is typically expressed in yearly terms, and it may either be an absolute number ($0.3000) or a fraction of the initial value (8.2%).
In general, volatility refers to the degree of unpredictable change over time of a certain currency pair exchange rate. It reflects the degree of risk faced by someone with exposure to that currency pair.
Volatility for market players
Volatility is often viewed as a negative in that it represents uncertainty and risk. However, higher volatility usually makes Forex trading more attractive to the market players. The possibility for profiting in volatile markets is a major consideration for day traders, and is in contrast to the long term investors’ view of buy and hold.
Volatility does not imply direction. It just describes the level of fluctuations (moves) of an exchange rate. A currency pair that is more volatile is likely to increase or decrease in value more than one that is less volatile.
For example, a common “conservative” investment, like in savings account, has low volatility. It will not lose 30% in a year but neither will it profit 30%.
Volatility over time
Volatility of a currency pair changes over time. There are some periods when prices go up and down quickly (high volatility), while during other times they might not seem to move at all (low volatility).
Source: Easy Forex
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)