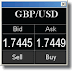
What are currency pairs? In the foreign exchange market, currency is traded in pairs. Pairs have meaning in relation
Friday, September 18, 2009
Thursday, September 3, 2009
easy forex, foreign exchange, forex, rewards, risks
Risks and Rewards in the Forex Market
In the Forex market, risks might be great, but the rewards can be great too. The Forex market is
foreign exchange, forex, volatile
Volatality in Forex
Volatility (in Forex trading) refers to the amount of uncertainty or risk involved with the size of changes in
Tuesday, August 25, 2009
easy forex, foreign exchange, forex, pip, spread
Pips and spreads
Pips and spreads show the value of a currency pair to the investor and to the broker. What is
agent, foreign exchange, forex, market maker
Forex Market Maker
What is a market maker? A market maker provides a platform for foreign currency exchange for the customer. Market
Friday, August 14, 2009
currency, foreign exchange, forex, online trading, trading
Leveraged Forex Trading
What is leverage in Forex trading? Traders in Forex trade a contract of currency exchange rates. As the movement
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)